Electrical Safety
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is a large regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor. OSHA’s mission is to “assure safe and healthy working conditions for working men and women by setting and enforcing standards and by providing training, outreach, education and assistance.
Electrical Safety (General Industry)
Relevant Regulations
OSHA’s electrical safety standards for general industry are included in 29 CFR 1910, Subpart S:
\(\bullet\) 1910.302 - 308, Design Safety Standards for Electrical Systems
\(\bullet\) 1910.331 - 335, Electrical Safety-Related Work Practices Standard
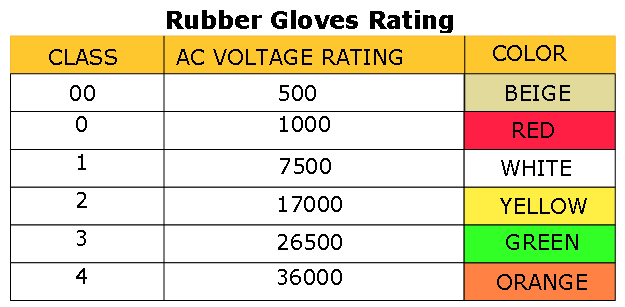
Generally, OSHA regulations require that companies keep workers and equipment, including cranes, scissor lifts, boom lifts, etc., at least 10 feet away from the overhead power lines to prevent contact.
Electricity creates a significant hazard in the workplace. Most injuries and fatalities result from:
\(\bullet\) Electric shock
\(\bullet\) Electrocution
\(\bullet\) Burns
\(\bullet\) Arc blasts
\(\bullet\) Fires
\(\bullet\) Explosions
If you encounter someone being shocked by electricity:
- Disconnect the power
- Call emergency medical services, or 911
- Don’t touch the victim unless you are certain that the power has been shut off. If you do, you may be the next victim!
- Use appropriate first aid and CPR techniques if you are trained to do so.
- Don’t touch bare wires, frayed wires, power lines, or power company equipment
- Don’t try to put out a fire started by electricity with water. Water can conduct electricity.
Before operating or working around electrical equipment, make sure you are properly trained. Do not install or repair equipment if you are not qualified. When operating or working around electrical equipment:
\(\bullet\) Respect the power of electricity
\(\bullet\) De-energize electrical equipment when working on it
\(\bullet\) Inspect and maintain equipment and tools
\(\bullet\) Use available safety features, like three-pronged plugs, tools that are double-insulated, and safety switches
\(\bullet\) Make sure electrical equipment is properly grounded
\(\bullet\) Follow lockout and tagging procedures
\(\bullet\) Use “C” rated extinguishers for electrical fires. Never use water.
\(\bullet\) Practice good housekeeping: care for cables and cords by keeping them clean and storing them properly
\(\bullet\) Do not touch water, bare wires, or ungrounded metal if you are not protected
\(\bullet\) Wear appropriate personal protective equipment for the job
\(\bullet\) Do not wear clothing or jewelry that can conduct electricity
Grounding is a (secondary) method of protecting employees from electric shock. Choose either ground fault circuit interrupters or an assured equipment grounding conductor program to protect employees on construction sites.