Lab-3 Nodal Analysis
Name:___________________________
Date:____________________________
Objectives:
To analyze a multi-source system using nodal analysis.
To solve simultaneous equations using MATLAB.
Equipment and component:
Resistors:
2.2 kΩ (1), 3.9 kΩ (1), 4.7 kΩ (1), 6.8 kΩ (1), 10 kΩ (2)
Agilent DMM (on the bench)
Agilent Power supply (on the bench)
Breadboard, 3 pairs of banana/clip leads, Bag of Wires
Outcomes:
Enter the calculated/measured results and provide your response to the questions as the edit to this document.
Include hand calculations in the document. You don’t need to type them out, just insert the image of the work.
Submit to Brightspace.
Procedure:
1.Set up nodal equations for the circuit in Figure 3.1 and show the steps of your calculations in a separate piece of paper and paste it at the end of your lab report. Use MATLAB to solve for the node voltages. Record the calculated values in Table 3-1.
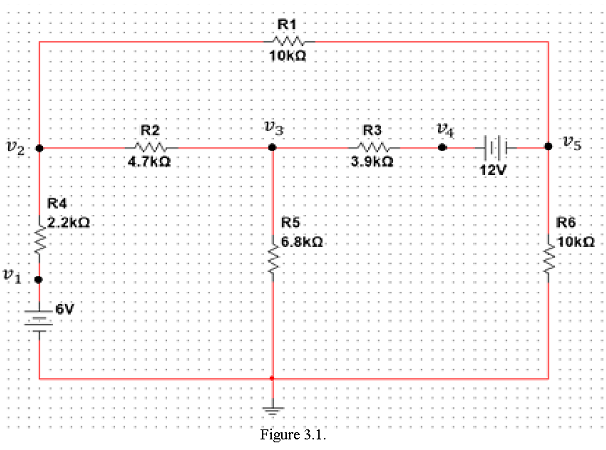
Construct the circuit using the bench power supply and other supplied parts. Make sure that the circuit is properly grounded. If you run out of banana-to-clip lead, use jumper wire to establish the ground connection.
Measure the node voltages using the DMM, and record the measurement in Table 3-1.
Table 3.1 Calculated and measured node voltages.
| \(V_1\) | \(V_2\) | \(V_3\) | \(V_4\) | \(V_5\) | |
| Calculated (V) | |||||
| Measured (V) (Multisim) | |||||
| Measured (V) (Breadboard) |
- With the measured node voltages, determine the voltage across and current through each resistor. Record the results (only the magnitude the currents and voltages) in Table 3-2. Label the direction of the resistor currents in Figure 3.1.
Table 3.2 Calculated voltage across and current through the resistors using measured node voltages. voltages.
| \(R_1\) | \(R_2\) | \(R_3\) | \(R_4\) | \(R_5\) | \(R_6\) | |
| Voltage (V) | ||||||
| Current (mA) |
5.Use the DMM to measure the voltage across and current through each resistor. Record the measurement (only the magnitude of the currents and voltages) in Table 3-3.
Table 3.3 Measured voltage across and current through the resistors.
| \(R_1\) | \(R_2\) | \(R_3\) | \(R_4\) | \(R_5\) | \(R_6\) | |
| Voltage (V) | ||||||
| Current (mA) |